Stuffed Young Zucchini
Stuffed Young Zucchini
4 small zucchini, 5 to 6-inches long, 1 1/2-inches thick
2 tablespoons extra-virgin olive oil
12 crimini mushrooms, chopped
1 small to medium yellow onion, chopped
3 to 4 cloves garlic, grated or chopped
Salt and freshly ground black pepper
2 vine ripe tomatoes or Roma tomatoes, seeded and chopped
2 slices white toasting bread
Softened butter
A small handful flat-leaf parsley
A few sprigs fresh tarragon or a small handful basil leaves
3/4 cup shredded Parmigiano-Reggiano
1 egg, beaten
Heat the oven to 425 degrees F. Halve 4 of the small zucchini lengthwise and scoop out the seeds and soft center flesh with a spoon to produce a set of shallow shells to hold the stuffing. Reserve the center flesh. Arrange the small hulls in a baking dish. Drizzle with a little extra-virgin olive oil and season with salt and pepper, to taste. Chop the reserved zucchini flesh and set aside. Heat the remaining extra-virgin olive oil in a skillet over medium-high heat and sauté the mushrooms, onions and garlic for 5 minutes. Add in the reserved zucchini and tomatoes, season with salt and pepper, to taste and heat through for 1 minute, then remove from the heat. While the veggies cook, toast the bread in a toaster, then spread liberally with butter and tear into pieces. Add the bread to a food processor along with the parsley and tarragon or basil, and pulse into herb crumbs. Fold the herb crumbs into the veggies along with 1/2 cup Parmesan and the egg. Mound the zucchini stuffing in to the shells and roast for 15 minutes. Remove from the oven, sprinkle the tops with remaining cheese and broil for 2 to 3 minutes to brown.
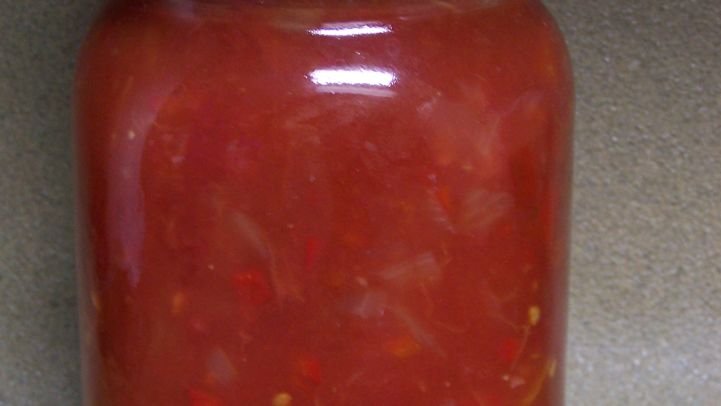
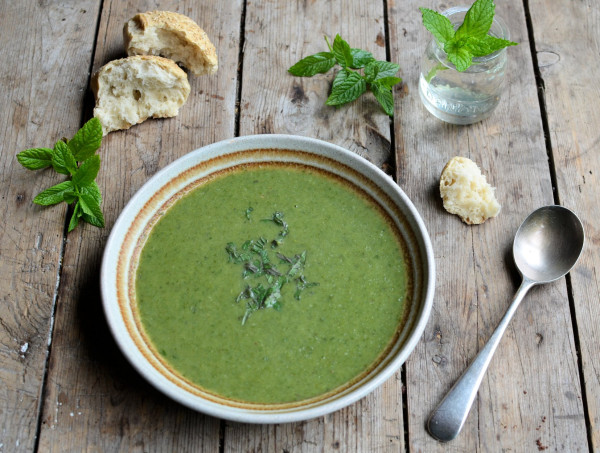
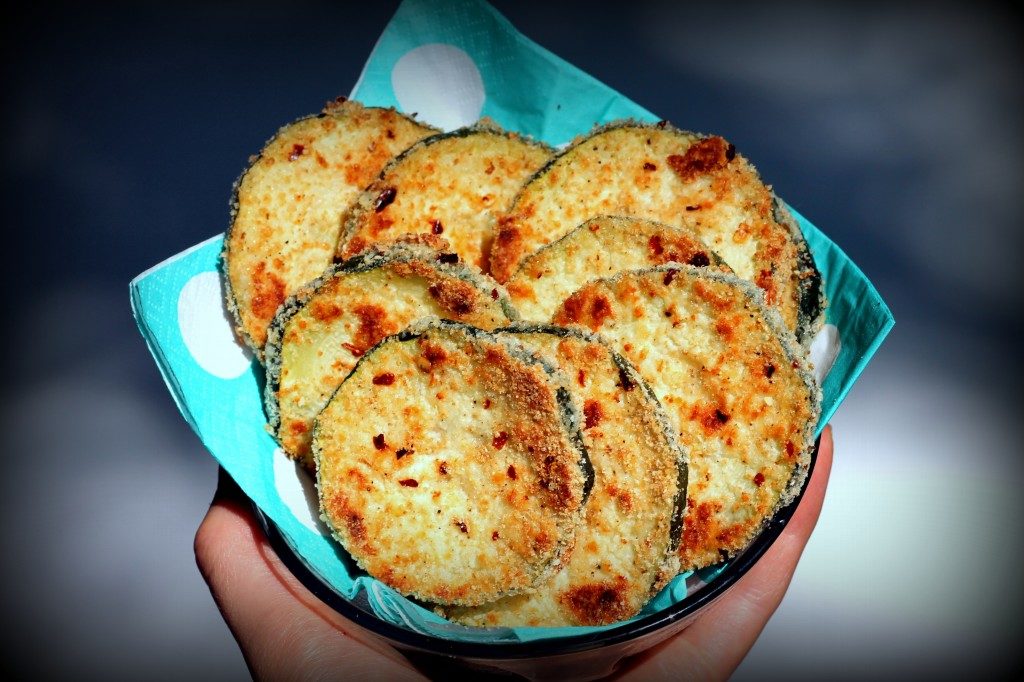
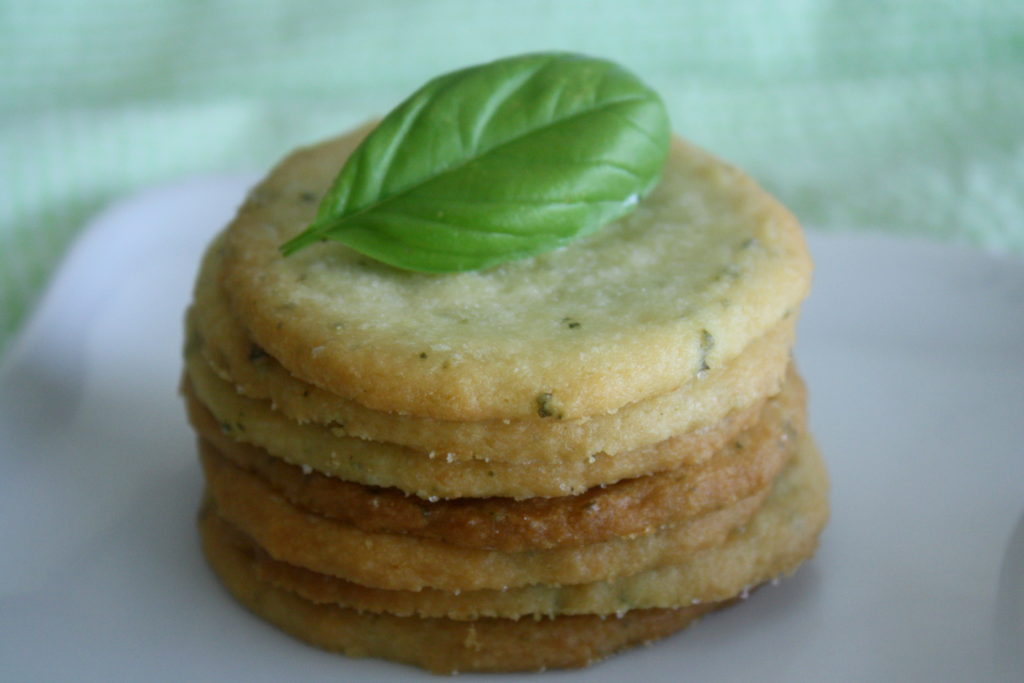
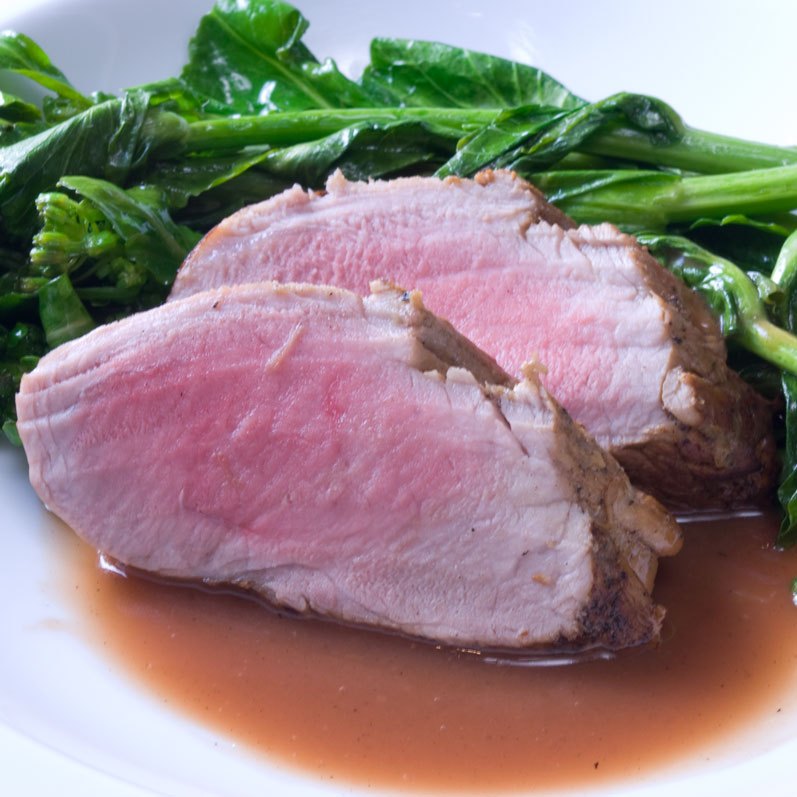
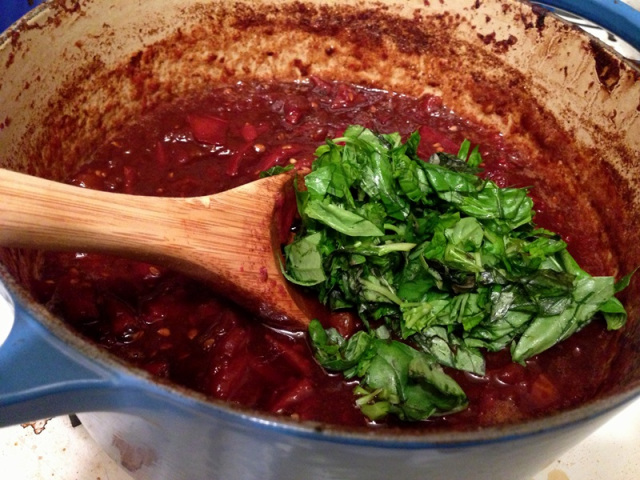
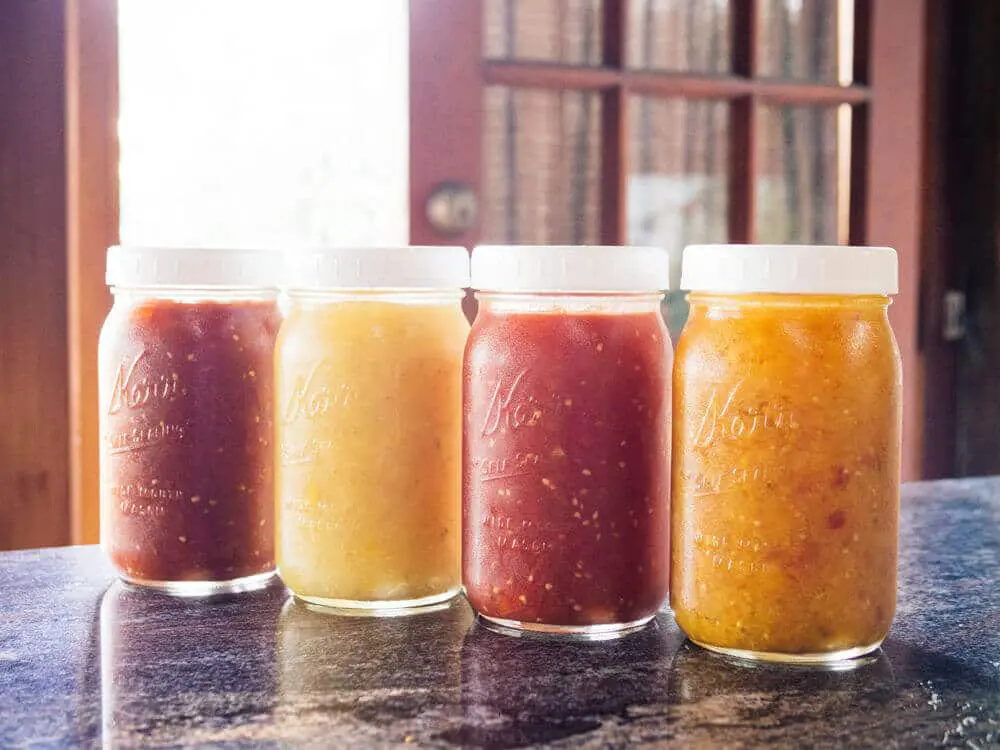






























 Easy Peasy Tomato Sauce
Easy Peasy Tomato Sauce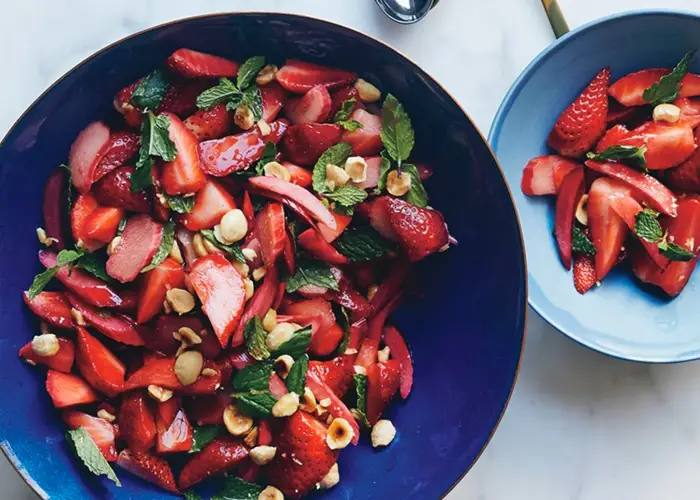 Strawberry-Rhubarb Salad with Mint and Hazelnuts
Strawberry-Rhubarb Salad with Mint and Hazelnuts